What Should You Know About Pregnancy And Hepatitis B
A pregnant woman who has hepatitis B can pass the infection to her baby at delivery. This is true for both vaginal and cesarean deliveries.
You should ask your healthcare provider to test you for hepatitis B when you find out you are pregnant. However, while it is important for you and your healthcare provider to know if you do have hepatitis B, the condition should not affect the way that your pregnancy progresses.
If you do test positive, your provider may suggest that you contact another healthcare provider, a liver doctor, who is skilled in managing people with hepatitis B infections. You may have a high viral load and may need treatment during the last 3 months of your pregnancy. A viral load is the term for how much of the infection you have inside of you.
You can prevent your infant from getting hepatitis B infection by making sure that your baby gets the hepatitis B vaccine in the hours after they are born along with the hepatitis B immunoglobulin. These two shots are given in two different locations on the baby. They are the first shots needed.
Depending on the type of vaccine used, two or three more doses must be given, usually when the baby is 1 month old and then 6 months old, with the last by the time the baby is 1 year old. It is critical that all newborns get the hepatitis B vaccination, but even more important if you have hepatitis B yourself.
What Should I Avoid While Receiving Hepatitis B Immune Globulin
Do not receive a “live” vaccine while using hepatitis B immune globulin, and for at least 3 months after your treatment ends. The vaccine may not work as well during this time, and may not fully protect you from disease. Live vaccines include measles, mumps, rubella , rotavirus, typhoid, yellow fever, varicella , zoster , and nasal flu vaccine.
You can safely receive a hepatitis B vaccine during your treatment with hepatitis B immune globulin.
Serological Markers Of Infection
The HBV antigens and their associated antibodies are serological markers of HBV infection or vaccination . At least one serological marker is present during the different phases of infection .
|
Antigen |
|---|
|
Immune if 10 IU/L vaccinated or natural infection |
Key: Anti-HBc = antibody to hepatitis B core antigen anti-HBs = antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen IgM = immunoglobulin M + = positive test result = negative test result.
Adapted from: Van Damme P, Ward J, Shouval D, et al. 2018. Hepatitis B vaccines. In: Plotkin SA, Orenstein WA, Offit PA . Plotkins Vaccines . Philadelphia, US: Elsevier. Table 25.1.
Any difficulties with interpreting serological results for cases and contacts should be discussed with an infectious diseases physician or the laboratory. See the Hepatitis B chapter of the Communicable Disease Control Manual for recommendations for HBV case and contact management.
You May Like: What Are The Early Signs Of Hepatitis
What Is Involved In A Liver Transplant
A liver transplant is considered necessary when the liver is damaged and cannot function or in some cases of liver cancer. Your liver is very important. It is responsible for many functions related to making sure that your body stays healthy and is able to digest foods.
You may be eligible for a transplant if you have chronic hepatitis B infection or some of the diseases that may result from it, including liver cancer and cirrhosis. You will have to complete testing and be evaluated before being approved for a transplant. It is likely that you will be placed on a waiting list while an appropriate organ is found.
Donated livers come from two types of donors: living and deceased. Because the liver can regenerate, it is possible to use part of a liver for transplant. The remaining sections in both the donor and the receiver will grow into livers of adequate size.
People who get liver transplants must take anti-rejection drugs for the rest of their lives. These drugs make you more susceptible to infection. However, liver transplants have become more successful over time and continue to improve.
Comparison Of Responses To A Hepatitis B Vaccine Challenge Dose Among Students With < 10 Iu/liter At The Baseline: Baseline Anti
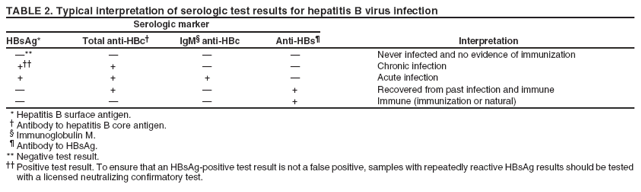
Of the 153 students who completed the study, 131 had an anti-HBsAg level of < 10 IU/liter at the baseline 73 had a level of 0 IU/liter, and 58 had levels of 1 to 9 IU/liter . Thirty-six of 73 with a level of 0 IU/liter and 48 of 58 with levels of 1 to 9 IU/liter responded to the challenge dose . Relative to those with a baseline anti-HBsAg level of 0 IU/liter, students with levels of 1 to 9 IU/liter were more likely to respond to the challenge dose . The anti-HBsAg GMCs after the challenge dose among students whose baseline anti-HBsAg level was 0 IU/liter versus those with baseline anti-HBsAg levels of 1 to 9 IU/liter were 9.8 IU/liter and 99.8 IU/liter , respectively . Among the 58 students with anti-HBsAg levels at the baseline ranging from 1 to 9 IU/liter, 21 had a level of 3 IU/liter of these 21 students, 20 responded to the challenge dose.
You May Like: What Is Hepatitis C Ab Test
How Common Is Hepatitis B
Hepatitis B is fairly common in Africa and the western Pacific region. Throughout the world, there are about 292 million people who are infected with chronic hepatitis B. In the U.S., the figure exceeds 2 million people.
The number of infections had been falling in the U.S., but fewer vaccinations among adults combined with the onset of the opioid crisis and injected drug usage has resulted in the numbers rising again. Infected women can pass the infection on to their babies. Children who are infected before age 5 are more likely to have chronic infection than those infected later in life.
Treatments For Hepatitis B
Treatment for hepatitis B depends on how long you have been infected for.
If you have been exposed to the virus in the past few days, emergency treatment can help stop you becoming infected.
If you have only had the infection for a few weeks or months , you may only need treatment to relieve your symptoms while your body fights off the infection.
If you have had the infection for more than 6 months , you may be offered treatment with medicines that can keep the virus under control and reduce the risk of liver damage.
Chronic hepatitis B often requires long-term or lifelong treatment and regular monitoring to check for any further liver problems.
Don’t Miss: Ways To Catch Hepatitis C
Who Are Hepatitis B Carriers
Hepatitis B carriers are people who have the hepatitis B virus in their blood, even though they dont feel sick. Between 6% and 10% of those people whove been infected with the virus will become carriers and can infect others without knowing it. There are over 250 million people in the world who are carriers of HBV, with about 10% to 15% of the total located in India. Children are at the highest risk of becoming carriers. About 9 in 10 babies infected at birth become HBV carriers, and about half of children who are infected between birth and age 5 carry the virus. A blood test can tell you if you are a hepatitis B carrier.
Where Can I Get More Detailed Information On How To Live With Hepatitis B
More detailed information can be found in the Canadian Liver Foundations Healthy Living with Viral Hepatitis booklet, including:
- What to expect if you have hepatitis B
- The different types of blood tests and what they measure
- How to prepare for an appointment with your doctor
- What choices to make to prevent additional damage to your liver
- Who needs to know if you have hepatitis B and how to tell them
- How to recognize and deal with symptoms
- How to find financial assistance
- What questions to ask when considering alternative therapies.
Don’t Miss: What Blood Test Checks For Hepatitis C
Profiles Of Stool Bacteria With And Without Antibiotic Treatment
Intestinal microbiota of the C3H/HeN mice reached equilibrium between 6 and 11 wk of age. The C3H/HeN mice were divided into two groups, one of which was treated with antibiotics and one of which was not . ABX mice received antibiotics in their drinking water between 5 and 12 wk of age, and their body weights were recorded. The amount of bacteria 16S rRNA was reduced 100-fold after antibiotic treatment. The profiles of intestinal microbiota, examined using TTGE, varied considerably between 6 and 9 wk of age in an untreated adult mouse and thereafter reached equilibrium. The ABX mouse showed an extremely low amount of bacteria, which did not vary in the course of treatment. M: 100-bp ladder marker dpi: days postinjection wpi: weeks postinjection.
Persons New To Canada
Health care providers who see persons newly arrived in Canada should review the immunization status and update immunization for these individuals, as necessary. In many countries outside of Canada, HB vaccine is in limited use.
All persons from a country that is endemic for HB should be assessed and vaccinated against HB if not immune and not infected. Individuals born in developing countries are more likely to be carriers of HB, necessitating vaccination of their sexual and household contacts based on review of their serologic test results. HB vaccine is recommended for all household contacts whose families have immigrated to Canada from areas in which there is a high prevalence of HB and who may be exposed to HB carriers through their extended families or when visiting their country of origin.
Children adopted from countries in which there is a high prevalence of HB infection should be screened for HBsAg and, if positive, household or close contacts in the adopting family should be immunized before adoption or as soon as possible thereafter. Adults going to pick-up children from these countries should be vaccinated before departure. Refer to Immunization of Persons New to Canada in Part 3 for additional information.
Recommended Reading: How Do You Contract Hepatitis B
Hydrodynamic Injection And Serum Collection
HBV expression plasmid pAAV/HBV1.2 was described previously . Before HDI, all animals were anesthetized using ketamine and xylazine administered by intramuscular injection. Ten micrograms of pAAV/HBV1.2 dissolved in 8% body weight of PBS was injected into the tail veins of the mice. The injection time was controlled between 5 and 7 s. Approximately 150 µL of serum was collected on days 2, 7, 10, and every week following HDI until the end of the experiment. Serum HBsAg and anti-HBs were measured using an AXSYM system kit . The anti-HB measurements were absolute values, whereas the HBsAg measurements were relative values. The HBsAg-positive threshold was set at an S/N ratio of 10 . Statistics were calculated using GraphPad Prism and Microsoft Excel.
The Immune System And Its Role In Hepatitis
The immune system is a collection of organs, cells, and tissues that work together to protect your body from pathogens that can cause disease. Its a very complex defense system that not only helps your body respond to infectious diseases , but it can also cause trouble in the form of allergies and autoimmune diseases.
Autoimmune diseases are the result of a process in which the immune system mistakes an organ or body system for an invader, and attacks it as such. This results in inflammation and damage to the organ.
Read Also: Hepatitis C Genotype 2b Treatment
Stool Dna Extraction And Ttge
Stool samples were freshly collected from each mouse every week using clean, autoclaved Eppendorf tubes and were stored at â80 °C before use. DNA was extracted from 0.4 to 0.5 g of stool using a QIAamp DNA Stool Mini Kit . DNA was recovered with 30 µL of elution buffer provided by Qiagen. The quality of the DNA was checked using gel electrophoresis, and the quantity of the DNA was measured using Nanodrop .
The V3 region of the bacteria 16S ribosomal RNA gene was amplified using F341GC and R534 primers . To avoid potential amplification bias, PCR was conducted in triplicate for each sample, and the products were pooled. TTGE was carried out using the DCode Universal Mutation Detection System . Ten microliters of PCR product was mixed with 10 µL of DNA loading dye, loaded onto acrylamide gel , and run for 6 h. The running temperature was set between 55 °C and 70 °C.
Persons With Inadequate Immunization Records
Evidence of long term protection against HB has only been demonstrated in individuals who have been vaccinated according to a recommended immunization schedule. Independent of their anti-HBs titres, children and adults lacking adequate documentation of immunization should be considered susceptible and started on an immunization schedule appropriate for their age and risk factors. Refer to Immunization of Persons with Inadequate Immunization Records in Part 3 for additional information.
Read Also: What Does It Mean To Have Hepatitis C Antibodies
Can Hepatitis B Be Controlled By Eating Right And Exercising
It is important that people with liver disease follow a healthy, nutritious diet as outlined by Health Canada in Eating Well with Canadas Food Guide.
Alcohol can also damage the liver so it is best that people with hepatitis B do not drink. Following a healthy lifestyle may also prevent fatty liver disease, another liver disease highly prevalent in Canada.
However, hepatitis B cannot be controlled by healthy eating and exercise alone. Hepatitis B can only be controlled by currently available treatment as prescribed by your doctor. Your doctor will need to do regular blood tests to know how much of the active virus is in your blood . The viral load test is used to monitor and manage hepatitis B patients. Viral load can tell your doctor if you need treatment for hepatitis B and how well you are responding to treatment.
Innate Immunity Against Hbv
Following initial infection, HBV DNA is detectable within 47 weeks, viral replication peaks at 810 weeks, and liver injury develops after 12 weeks . Individuals with an exceptionally overactive immune response against the rapid growth of HBV mutants develop fulminant hepatitis. In contrast with hepatitis C infection, studies of HBV-infected chimpanzees showed that HBV does not induce interferon-stimulated genes during the viral incubation phase. These results indicate that HBV potentially evades the host innate immune response by reducing its visibility to immunological surveillance mechanisms. Given that HBV replication is generally not detectable until about 4 weeks after HBV infection, innate immunity is predicted to be important for controlling virus replication.
Figure 1
Also Check: Drinking Alcohol With Hepatitis C
How Much Does A Hepatitis B Titer Test Cost
The cost of a hepatitis B test varies based on where you get the test. Prices range from roughly $24 to $110.
Your insurance may cover some or all of the cost. Under the Affordable Care Act, all new health plans must cover preventative services including hepatitis B vaccination and testing without a deductible or copay.
How Is Hepatitis B Spread
You can become infected with hepatitis B through exposure to blood, semen and other bodily fluids of an infected person. You can get the infection by:
- Having unprotected sex.
- Sharing or using dirty needles for drug use, tattoos or piercing.
- Sharing everyday items that may contain body fluids, including razors, toothbrushes, jewelry for piercings and nail clippers.
- Being treated medically by someone who does not use sterile instruments.
- Being bitten by someone with the infection.
- Being born to a pregnant woman with the infection.
Hepatitis B is not spread by:
- Kissing on the cheek or lips.
- Coughing or sneezing.
- Hugging, shaking hands or holding hands.
- Eating food that someone with the infection has prepared.
- Breastfeeding.
You May Like: Can Hepatitis B Cause Meningitis
Aboriginal And Torres Strait Islander People
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people are recommended to:
- have their risks and vaccination status for hepatitis B reviewed
- receive testing for previous hepatitis B virus infection
- receive vaccination if non-immune
Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander people have a higher risk of acquiring new hepatitis B virus infection than non-Indigenous Australians.2,3
Adult-formulation hepatitis B vaccine should be given in a 3-dose schedule.
Children with HIV are recommended to receive 3 doses of hepatitis B vaccine using an adult formulation. This is double the recommended dose for children. In a limited number of studies, children who were immunocompromised responded better when given higher doses in a 3-dose schedule.4,5
Levels of antibody to hepatitis B surface antigen should be checked after the vaccination course. See Serological testing after hepatitis B vaccination.
Adults with HIV are recommended to receive larger-than-usual doses of hepatitis B vaccine. They should receive 2 injections of the standard adult dose on each occasion at 0, 1, 2 and 6 months. Limited studies in adults with HIV have revealed an improved and accelerated serological response to a schedule that consists of 4 double doses.6,7
A 3-dose schedule at 6, 8 and 12 months after transplant is required using:
Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Test

A hepatitis B surface antigen test shows if youre contagious. A positive result means you have hepatitis B and can spread the virus. A negative result means you dont currently have hepatitis B. This test doesnt distinguish between chronic and acute infection. This test is used together with other hepatitis B tests to determine the .
Recommended Reading: How Do You Contact Hepatitis